Galileo Open Service Authentication (OSNMA)
Galileo is the European Global Satellite Navigation Satellite System. Similarly to GPS, it offers an Open Service signal which allows all users to calculate position, velocity and time free-of-charge.
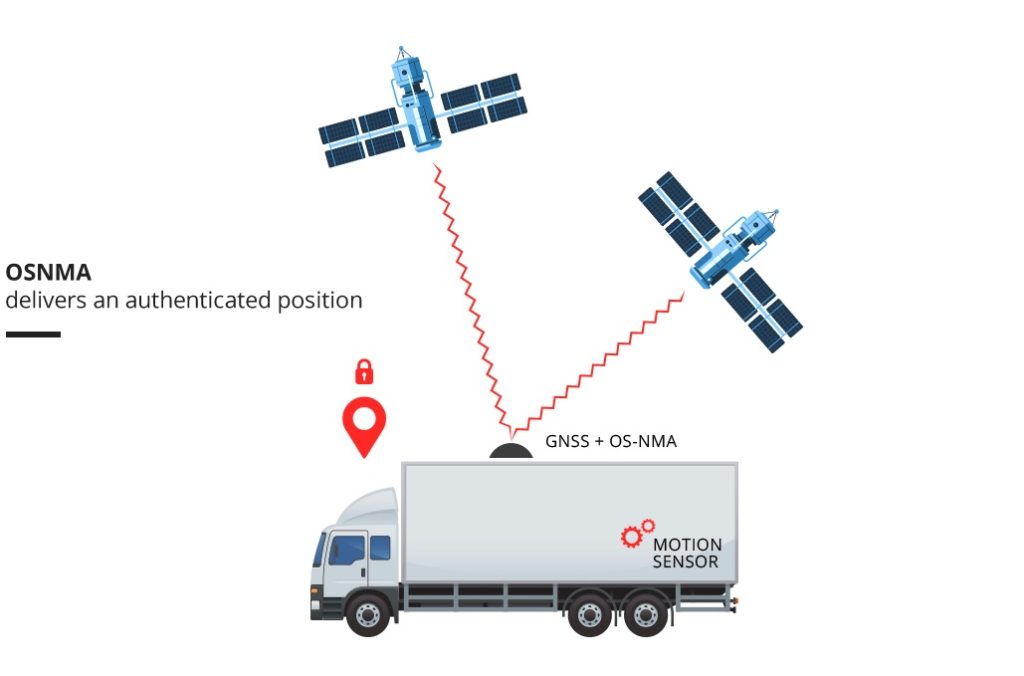
Moreover, Galileo will provide a new features that allows to authenticate the data received from the satellite, contributing to increase the overall security of applications and services. This feature is called Open Service Navigation Message Authentication (OSNMA) and is soon becoming operational, free of charge, for every user to benefit from. OSNMA solves many of the current threats that poses at risk GNSS receivers in civil applications, and guarantees that the received Galileo Open Service navigation data is authentic. From the technical point of view, OSNMA:
Validates the Navigation data (ephemeris, clock..) used by the GNSS receiver to compute the Position.
Provides, as side benefit, some form of protections against replay attacks through the insertion of unpredictable but verifiable symbols.
The introduction of OS-NMA contributes to strengthen the resilience of the PVT (Position, Velocity, Time) solution, in synergy with receiver based anti-spoofing mechanisms.
GNSS in smart tachographs
Since 2006, all European vehicles over 3.5 tonnes must be fitted with a digital tachograph, according to European regulations, with the aim to guarantee the safety and working conditions of drivers. Digital tachographs provide enforcers with a witness of the drivers’ driving times, break and rest periods.
From the technical point of view, the new regulations for Smart Tachographs (EU – No 165/2014 and 799/2016 and 502/2018) require the use of Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), like GPS and Galileo, for:
The provisioning and recording of vehicle positions.
The recording of the vehicle’s position declared by drivers at start / end of their daily work period.
The automatic recording of the vehicle’s position, each time the accumulated driving time reaches 3h.
Securing the speed provided by the motion sensor of the vehicle (to be corroborated by vehicle motion information derived from the GNSS receiver).
Securing time.
Triggering events (absence of position information from GNSS receiver, vehicle motion conflict, time conflict).
After mid-June 2019, the use of GNSS (Global Satellite Navigation Systems) is mandatory in all new vehicles where the Regulation (EU) 561/2006 is applicable (commercial vehicles above 3.5t, or transporting more than 9 persons). The smart tachograph regulation requires that the GNSS receivers used by smart tachographs are compatible with the services provided by Galileo and EGNOS. GNSS receivers must be capable to support the upcoming Galileo Open Service Authentication (OSNMA) when it will be provided by Galileo and supported by GNSS receiver manufacturers.